Table of Contents
Shear wall
It is the vertical structural element of a reinforced concrete framed structure which is provided to resist in-plane lateral loads such as wind, earthquake or sometimes due to hydro-statics or lateral earth pressure. Shear walls are often provided to multi-storey or tall building or the buildings in areas of high wind velocity and seismic activity. A typical example of shear wall in the building is the lift well. They resist the in-plane shear and in-plane flexural moment caused by lateral loads through the vertical Cantilever Action.
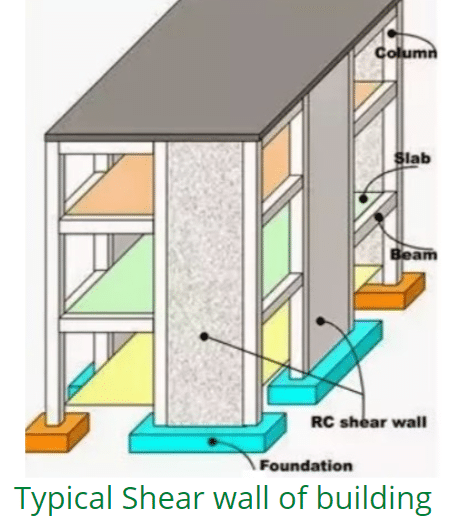
Due to lateral loads, buildings move or sway horizontally. And this effect increases significantly with rise in the height of reinforced concrete frame structure. Different codes set the limit of lateral deflection due to horizontal movement caused by lateral loads. Most of the code states that the relative lateral drift in any one storey shall not be exceed 0.2 – 0.4 % of the height of that storey.
Why should the lateral deflection be limited to 0.2% of storey height?
The lateral deflection is limited to prevent
- an adverse effect on the behavior of non-load bearing elements
- degradation in the appearance of the building
- discomfort feeling for the occupant
- limitation on the use of building
Material used for shear wall construction:
To meet all the requirements, shear wall is usually made of structural steel or of reinforced concrete. Though it may also be made using plywood or masonry structure.
In most of the cases, the walls are constructed by brick, or concrete block. And these walls are less resistance against lateral loads. So, They are designed mostly to resist the lateral loads.
Functions:
- It provides lateral shear strength to the building to resist the horizontal earthquake forces, wind forces and transfer these forces to the foundation.
- It provides large strength and stiffness to building in the direction of their orientation
- It reduces lateral sway of the building and thus reduces damage to structure.
The main advantage of having shear wall is that the size of column and beam can be drastically reduced. And the disadvantage is no opening can be placed in it.
Arrangement and design configuration:
A shear wall may be built around a building along its outer periphery. Such arrangement are simpler and provide good strength and stiffness to the structure.
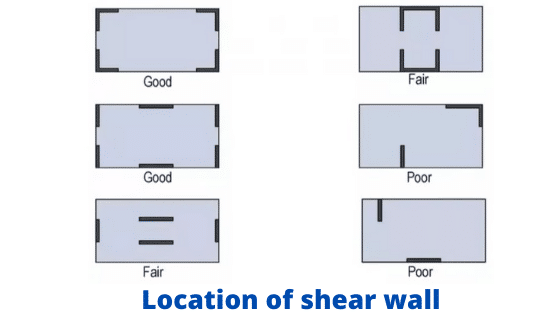
Location of Shear Wall in building
- Symmetry can be along one or both direction
- Can be located at exterior or interior
- Generally provided in lift pit and outer walls or in any portion inside a frame
- For the best torsional resistance, as many of the wall as possible should be located at the periphery of the buildings as it increase moment of inertia.
For maximum efficiency and economy, they should be provided at the periphery of the building.
Shear walls are aligned in the direction of the force to generate higher stiffness compared to column. They are more efficient when they are combined with frames. There is enhancement of lateral capacity of the structure when the wall frame intersection is considered.
The location is purely dependent on the plan of structure, the core location, the symmetry of the building and the lateral for experience by the structure. In case of difficulties in deciding the best location, analysis of different positions is done and the best option is chosen.
Why symmetrical?
Lateral loads tend to act along the direction of movement of wind or vibrations of the earthquake and they act laterally to the building along one of the two directions. Since shear wall resists in-plane shear and in-plane flexural bending, it should be provided symmetrically in both side. It should be placed symmetrically to avoid the ill effect of twisting. The symmetricity will help to avoid torsion and ensure the match of center of stiffness with center of mass of building.
Why is shear wall provided around the lift and staircase?
For efficient load transfer, shear wall should extends from bottom to top without any opening or discontinuity. It is provided in three side of the lift wall and one side is left for entry and exit from the lift.
Stairway and elevator cores are natural locations for structural walls, which serves a dual purpose of enclosing vertical shaft while providing efficient axial and lateral resistance.
The provision of shear wall as a lift and staircase wall has following advantages,
- It supports the horizontal earth pressure below the floor level.
- It prevents the seepage of water into lift pit.
- A concrete wall provides better anchorage as lift frames are drilled to the wall.
- The anchorage length bars are left on which the stairs can be made and load can be beard by these walls.
Shear wall building are more popular choice in many earthquake prone countries. They are efficient, both in terms of construction cost and effectiveness in minimizing earthquake damage in structural and non-structural elements like glass windows and building contents.
What should be done if shear wall can’t be provided along both axis?
If shear wall are provided along just one direction, a correct grid of beams and column in vertical plane must be provided along other direction to resist strong earthquake effects.
Codal Provision: [IS 13920:2016]
- Thickness shall not be less than
- 150 mm and
- 300 mm for building with coupled shear wall in any seismic zone
- Minimum ratio of length of wall to its thickness shall be 4.
- Classified as squat, intermediate or slender depending on the overall height (hw) to length (lw) ratio as
- Squat walls: (hw/ lw)<1
- Intermediate walls: 1≤(hw/ lw)≤2
- Slender walls: (hw/ lw)>2
- Provide uniformly spaced minimum reinforcement 0.25% of gross area in each direction
- Reinforcement bar shall be provided in two curtains within the cross section of wall, with each curtain having bars running along vertical and horizontal direction, when
- Factored shear stress demand in the wall exceed 0.25(fck)1/2 MPa, or
- Wall thickness is 200 mm or higher
- Diameter of reinforced bar shall not exceed 1/10 th of thickness of section
- Special shear wall shall be founded on properly designed foundations and shall not be discontinued to rest on beams, columns or inclined members.
ALSO READ

