Slump Test of concrete is performed to measure the degree of workability (ie. consistency) of freshly made concrete.
| Degree of Workability | Slump Value |
| Very Low | <25 |
| Low | 25-75 |
| Medium | 50-100 |
| High | 100-150 |
| Very High | >150 |
Table of Contents
Table Of Content
| 1. Introduction 2. Importance of slump test 3. Types of slump 4. Apparatus Required 5. Procedure of this test 6. Some Important related questions |
1. Introduction of Slump Test
Slump test is assessment of the workability of concrete in the field. Greater the slump value, Greater is the workability.
The slump value is the settlement of the concrete after the removal of cone. It simply means the difference of original cone height (300 mm) and the height of concrete after the removal of cone. The increase in water-cement ratio gives higher value of slump.
2. Importance of Slump Test
Slump test is the field test of workability of concrete. And workability of concrete is important because, if
- the concrete mix is too wet, coarse aggregate settle at the bottom of concrete mass and as a result concrete becomes non-uniform composition.
- the concrete is too dry, it will be difficult to handle and place it in position which will eventually lead honeycombing in the structure.
3. Types of Slump
The slump can be classified into following three groups from lower to higher value of slump:
True slump refers to decrease in height of the concrete mass evenly all around the slump cone without disintegration. If there is no drop of concrete on removal of slump mound then that type of concrete is called Zero slump concrete. The concrete with Zero slump value is generally used for road construction.
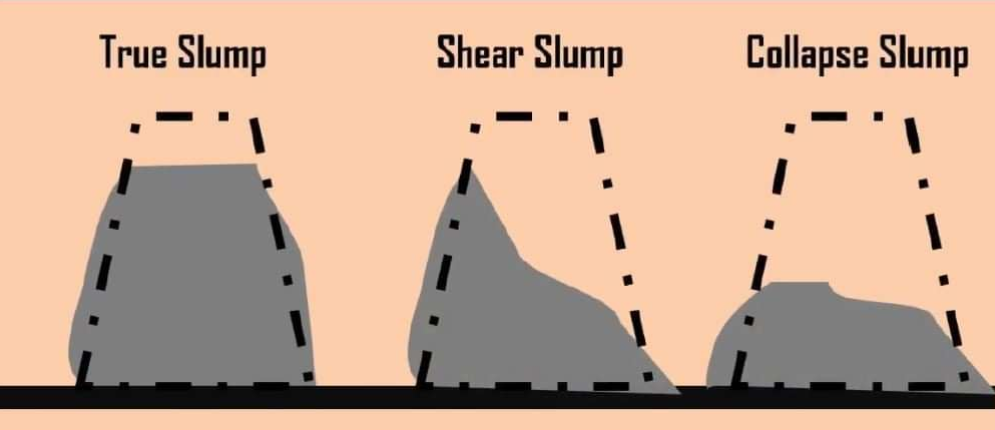
Shear slump indicates that lack of cohesion in concrete and tends to occurs harsh mixes. There is possibility of undergoing segregation and bleeding of this type of concrete so it is undesirable for durability of concrete.
Collapse Slump indicates that concrete is too wet and mix is regards to harsh and lean.
4. Apparatus for Slump Test
The tools required to perform the this test are:
- Slump cone and tamping rod
- Water proof base
- Trowel
- Measuring Tape
- Concrete mix
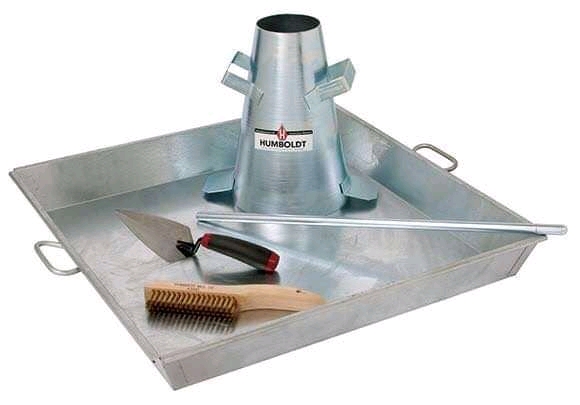

The dimension of slump cone is,
Top diameter = 100 mm
Base diameter = 200 mm
Height = 300 mm
The diameter of tamping rod should be 16mm and length 600mm.
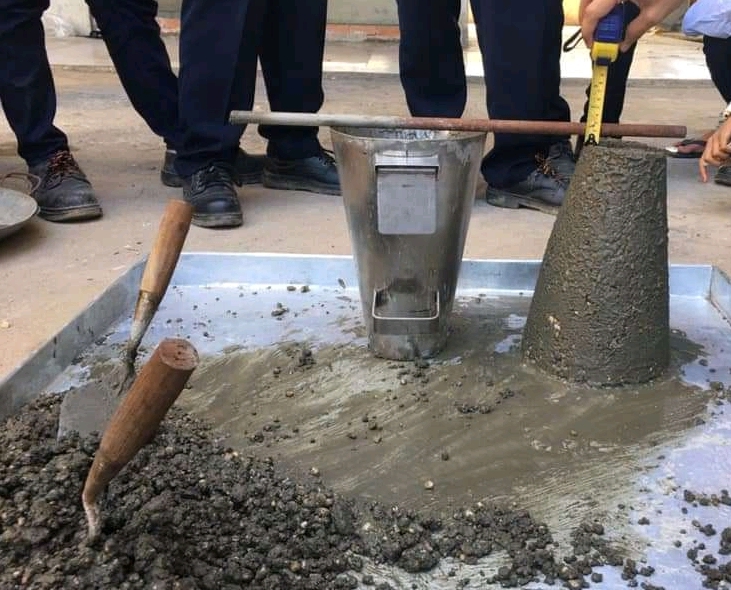
5. Procedure of Slump Test
- Place the slump cone on a level smooth waterproof base
- Place the nixed concrete in the cone to about one-fourth of the height ie. 75mm
- Compact concrete uniformly all over the area by 25 times with the help of tamping rod.
- Repeat the action of placing concrete 75mm and 25 times tamping for 3 more times until the cone is full and screed off the top
- Gently lift cone from the concrete ensuring its movement in perfectly vertical direction.
- Measure the subsidence of the concrete when the settlement of concrete stops.

6. Slump Test Result Interpretation:
The slump test will gives different types of slump results.
Case1. True Slump
The acceptable range of slump for different types of concrete is tabulated below. Increase the quantity of water if slump value is less than the acceptable range and vice versa.
| Slump Value | Degree of Workability | Placing condition |
| <25 | Very Low | Shallow section; Pavement using pavers |
| 25-75 | Low | Less Reinforced RCC section; Canal lining |
| 50-100 | Medium | Heavily reinforced RCC section |
| 100-150 | High | Pumped Concrete |
| >150 | Very High | In-situ piling; Termie concrete |
Note:
- Strict control is necessary for concrete with very low workability. The measurement of workability by determination of compacting factor will be more appropriate than slump for vary low category of Workability.
- The measurement of workability by determination of flow will be appropriate in case of very high degree of workability.
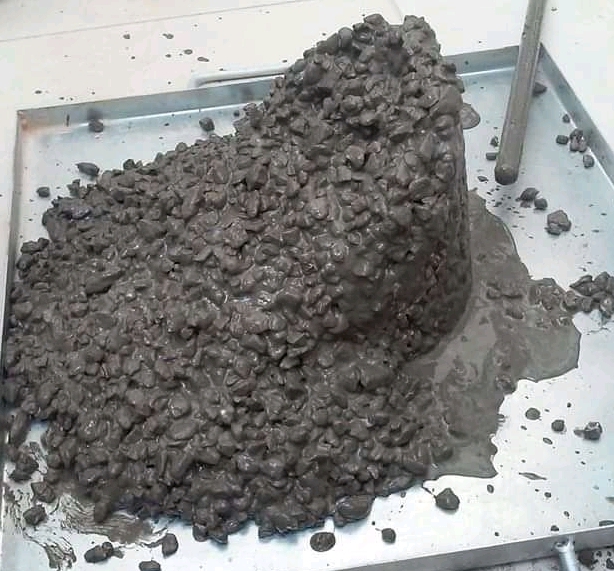
Case 2. Shear Slump
If the slump test gives the shear slump then Re-test with fresh concrete mixes. The test method usually advices that two consecutive shear slumps indicated that concrete should not be evaluated with slump test. It gives some indication that there is something wrong with the concrete, but it is not the deciding factor in most cases. There are plenty of other test to evaluate the concrete.

7. Some Important related questions
Some related questions are added soon on the basis of demands of viewers.
Also Read:

