As per IS code, the thickness of cover block should not be less than as follows;
- Raft Foundation = 75 mm for bottom and 50mm for top and sides
- Isolated Footing = 50 mm
- Strap Beams = 50mm
- Column = 40 mm
- Beams = 25 mm
- Slabs = 15-20 mm
- Shear Wall = 25mm
- Retaining Wall = 20-25 mm on earth
- Water Retaining Structure = 20-30 mm
Read complete for more details.
| Table of Content |
| 1. Definition 2. Reason of Providing 3. Criteria of Providing 4. Making Concrete block in sites 5. Some important related questions |
Table of Contents
1. Definition of Cover Block
A cover block is essentially a spacer which gives the some gap between the reinforcement bar and the formwork or finished surface of RCC members. Different types of cover block are available in the market in terms of materials (plastic or cement mortar) and depth.
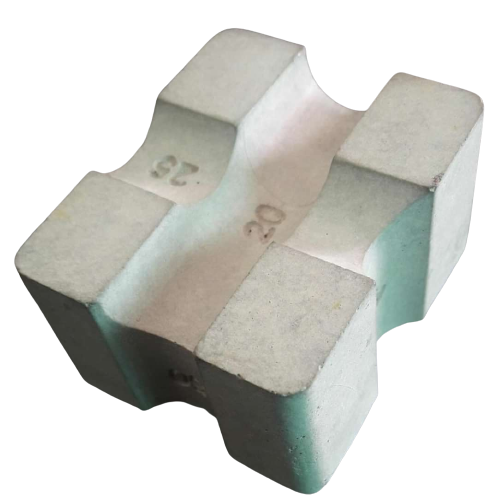

2. Reason of Providing Cover Block
Cover block is designed in order to provide clear cover in the structural RCC members. Corrosion of rebar can be prevented by encasing inside the concrete, and the cover blocks help in encasing. Following are the reason for providing cover blocks in RCC;
- Prevent corrosion of reinforcement of concrete
- Give fire protection to the reinforcement
- Add strength to life of concrete without increase in cost of concrete
- Maintain a straight alignment of steel
- Honeycombing of concrete can be avoided with proper arrangement of cover blocks during concreting.
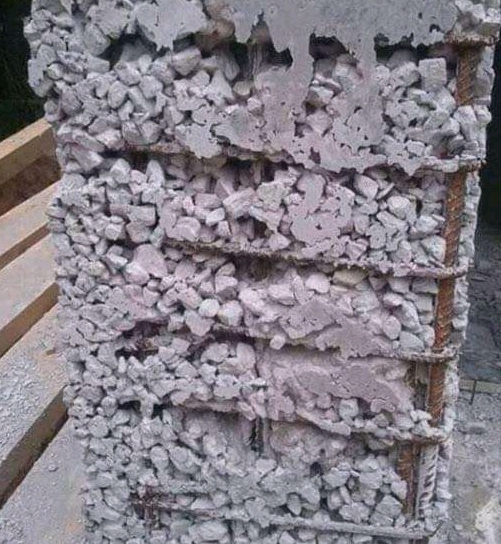

3. Criteria of Providing
The thickness of clear cover depends upon the types of structural members and exposure conditions.
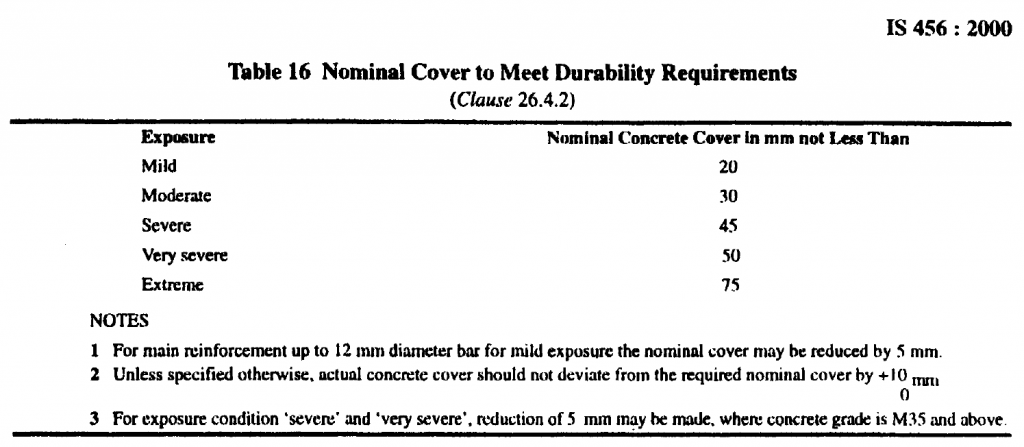
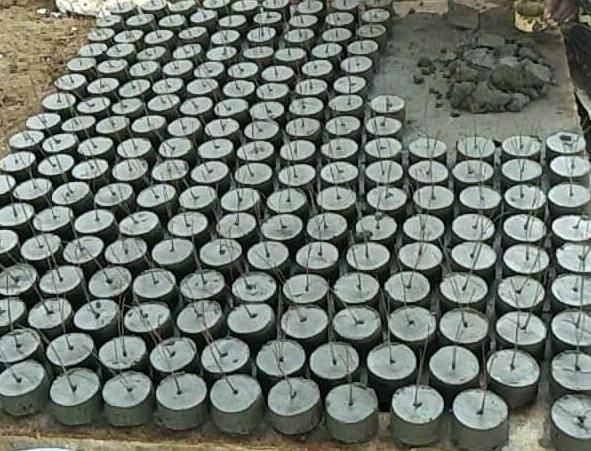
4. Making Concrete Cover block in sites
Cover blocks are available in market with minimum spent of cost. But sometimes it is not possible to bring cover blocks from the market. In such situation, we can’t continue construction without providing clear cover. Cover blocks can be made in the site with the material easily available in construction sites. While making concrete blocks in construction site, the strength of concrete blocks should be greater than the concrete using the RCC member. Normally, the concrete blocks are made with cement mortar of ratio 1:1 or 1:2.

5. Some important related questions:
Q1. How many cover blocks are provided in slab per square meter?
A. Normally 4 numbers. The spacing of concrete block in the slab depends upon the diameter of bar used in it. While placing cover blocks, it should be keep in mind that the reinforcement has uniform clear cover across the slab. If the spacing is less than required then the reinforcement sags and touch the shuttering. As per IS code, the minimum spacing between the cover block should be 700mm. But for effective use, it is recommended to provide spacing of 500-600 mm.
Q2. Why aggregate should not use to provide clear cover in RCC member?
A. It is found that there is wrong practice of providing aggregate for clear cover in RCC member. Due to following reasons, aggregate should not be used as cover block in RCC members:
- Aggregate can’t provide the uniform thickness of clear cover due to its un-uniform shape
- Difficulties to keep them in their position during concrete placing
- Slip from the position while using vibrator
Also Read:


