Dynamic Analysis
Dynamic analysis shall be performed to obtain the design lateral force (design seismic base shear, and its distribution to different levels along the height of the building and to the various lateral load resisting elements), for the following buildings:
a) Regular buildings with height in zone IV and V, greater than 40 m and height of 90 m in Zones II and III.
b) Irregular buildings (ie. all framed structure building) with height greater than 12 m in Zones IV and V and greater than 40 m in height in Zones II and III.
For dynamic analysis of buildings with unusual configuration, the analytical model should be made such that it can show the types of irregularities that is actually present in the building configuration.
NOTE: For irregular buildings having height lesser than 40 m in Zones II and III, dynamic analysis is recommended, even though not mandatory. The seismic analysis of the building structure shall be based on the IS code 1893 part 1 2016.
Dynamic analysis may be performed either by
- Time History Method or
- Response Spectrum Method.
Time History Method
Time history method of analysis should be based on an appropriate ground motion (preferably compatible with the design acceleration spectrum in the desired range of natural periods) when used. This method shall be carried out by using accepted principles of earthquake structural dynamics.
Response spectrum analysis
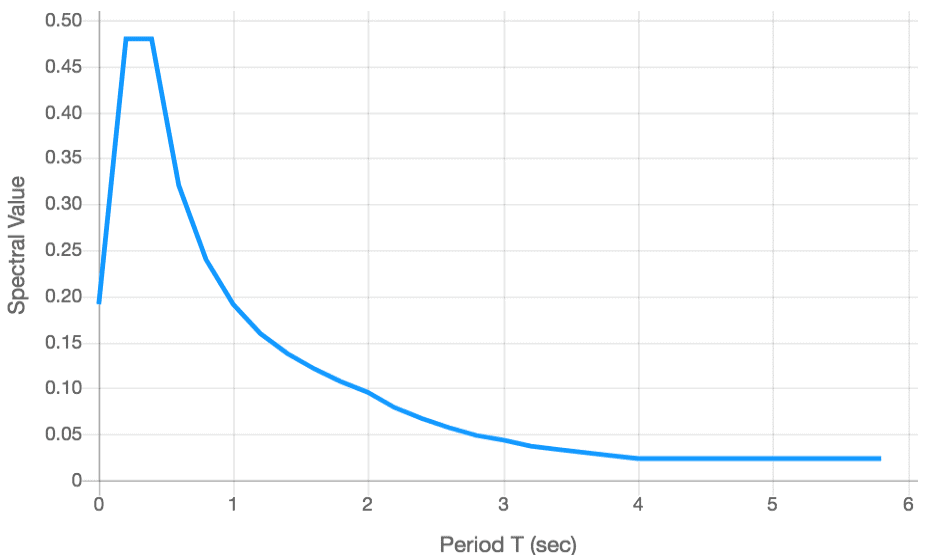
We can define Response-spectrum analysis as the linear-dynamic statistical analysis method that is used to indicate likely the maximum seismic response of an essentially elastic structure by measuring the contribution from each natural mode of vibration. In order to perform the seismic analysis and style of a structure to be built at a specific location, the particular time history record is required.
Source: skyciv.com
However, it’s impossible to possess such records at each and each location. Further, Based on the peak value of ground acceleration, the seismic analysis of structures can’t be carried out simply because the response of the structure depend on the frequency level of ground movement and its own dynamic properties. To overcome the above difficulties, earthquake response spectrum is that the hottest tool within the seismic analysis of structures. For the prediction of displacements and member forces in structural systems, there are computational advantages in using the response spectrum method of seismic analysis. The method involves the calculation of only the utmost values of the displacements and member forces in each mode of vibration using smooth design spectra that are the typical of several earthquake motions.
This work deals with response spectrum method and its application to varied sorts of the structures. The codal provisions as per IS: 1893 (Part 1)-2016 code for response spectrum analysis of multi-story building is also summarized.
ALSO READ